OceanRep
Biogeochemical conditions determine virulence of black band disease in corals.
Glas, Martin S, Sato, Yui, Ulstrup, Karin E and Bourne, David G
(2012)
Biogeochemical conditions determine virulence of black band disease in corals.
![]() The ISME Journal, 6
(8).
pp. 1526-1534.
DOI 10.1038/ismej.2012.2.
The ISME Journal, 6
(8).
pp. 1526-1534.
DOI 10.1038/ismej.2012.2.
Preview |
Text
ismej20122a.pdf - Published Version Available under License Creative Commons: Attribution 4.0. Download (475kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of ismej20122x1.jpg]](https://oceanrep.geomar.de/32232/3.hassmallThumbnailVersion/ismej20122x1.jpg) 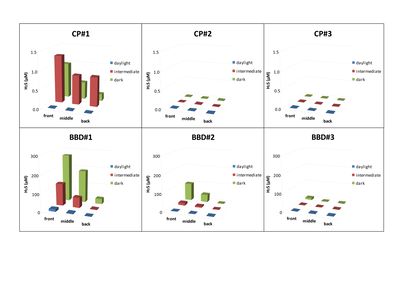 Preview |
Image
ismej20122x1.jpg - Supplemental Material Available under License Creative Commons: Attribution 4.0. Download (679kB) | Preview |
|
Text
ismej20122x2.doc - Supplemental Material Available under License Creative Commons: Attribution 4.0. Download (32kB) |
Abstract
The microenvironmental dynamics of the microbial mat of black band disease (BBD) and its less virulent precursor, cyanobacterial patch (CP), were extensively profiled using microsensors under different light intensities with respect to O(2), pH and H(2)S. BBD mats exhibited vertical stratification into an upper phototrophic and lower anoxic and sulphidic zone. At the progression front of BBD lesions, high sulphide levels up to 4977 μM were measured in darkness along with lower than ambient levels of pH (7.43±0.20). At the base of the coral-BBD microbial mat, conditions were hypoxic or anoxic depending on light intensity exposure. In contrast, CP mats did not exhibit strong microchemical stratification with mostly supersaturated oxygen conditions throughout the mats at all light intensities and with levels of pH generally higher than in BBD. Two of three replicate CP mats were devoid of sulphide, while the third replicate showed only low levels of sulphide (up to 42 μM) present in darkness and at intermediate light levels. The level of oxygenation and sulphide correlated well with lesion migration rates, that is virulence of the mats, which were greater in BBD than in CP. The results suggest that biogeochemical microgradients of BBD shaped by the complex microbial community, rather than a defined pathogen, are the major trigger for high virulence and the associated derived coral mortality of this disease.
| Document Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Keywords: | BBD; CP; pathogen; microsensor; anoxia; sulphide |
| Refereed: | Yes |
| Open Access Journal?: | No |
| Publisher: | Nature Publishing Group |
| Projects: | BIOACID |
| Date Deposited: | 29 Apr 2016 12:09 |
| Last Modified: | 29 Apr 2016 12:09 |
| URI: | https://oceanrep.geomar.de/id/eprint/32232 |
Actions (login required)
 |
View Item |
Copyright 2023 | GEOMAR Helmholtz-Zentrum für Ozeanforschung Kiel | All rights reserved
Questions, comments and suggestions regarding the GEOMAR repository are welcomed
at bibliotheksleitung@geomar.de !


 Tools
Tools Tools
Tools
