OceanRep
Population attenuation in zooplankton communities during transoceanic transfer in ballast water.
Ghabooli, Sara, Zhan, Albin, Paulucci, Esteban, Hernandez, Marco R., Briski, Elizabeta  , Cristescu, Melania E. and MacIsaac, Hugh J.
(2016)
Population attenuation in zooplankton communities during transoceanic transfer in ballast water.
, Cristescu, Melania E. and MacIsaac, Hugh J.
(2016)
Population attenuation in zooplankton communities during transoceanic transfer in ballast water.
![]() Ecology and Evolution, 6
(17).
pp. 6170-6177.
DOI 10.1002/ece3.2349.
Ecology and Evolution, 6
(17).
pp. 6170-6177.
DOI 10.1002/ece3.2349.
Preview |
Text
ece32349.pdf - Published Version Available under License Creative Commons: Attribution 3.0. Download (670kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Image (Protocol for analysis of 19 ballast water samples collected during three Atlantic voyages)
ece32349-sup-0001-FigS1.tif - Supplemental Material Available under License Creative Commons: Attribution 3.0. Download (5MB) | Preview |
Preview |
Image (Neighbor-joining tree for all OTUs recovered from voyage one)
ece32349-sup-0002-FigS2.tif - Supplemental Material Available under License Creative Commons: Attribution 3.0. Download (1MB) | Preview |
Preview |
Image (Neighbor-joining tree for all OTUs recovered from voyage two)
ece32349-sup-0003-FigS3.tif - Supplemental Material Available under License Creative Commons: Attribution 3.0. Download (1MB) | Preview |
Preview |
Image (Neighbor-joining tree for all OTUs recovered from voyage three.)
ece32349-sup-0004-FigS4.tif - Supplemental Material Available under License Creative Commons: Attribution 3.0. Download (2MB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Sample-based rarefaction curves from the initial (red lines), middle (green), and final (blue) sampling and 95% confidence intervals (dashed lines).]](https://oceanrep.geomar.de/32991/11.hassmallThumbnailVersion/ece32349-sup-0005-FigS5.jpg) 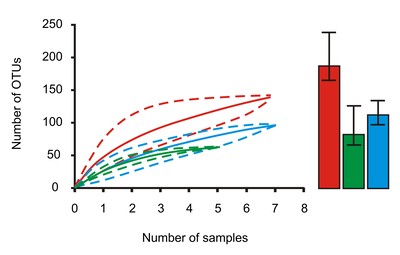 Preview |
Image (Sample-based rarefaction curves from the initial (red lines), middle (green), and final (blue) sampling and 95% confidence intervals (dashed lines).)
ece32349-sup-0005-FigS5.jpg - Supplemental Material Available under License Creative Commons: Attribution 3.0. Download (1MB) | Preview |
|
Text (able S1. Environmental characteristics (temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen (D.O.), and salinity) of three ballast water (A, B, and C) samples obtained at the initial (int), middle (mid), and final (fin) day during three voyages of a vessel transiting...)
ece32349-sup-0006-TableS1-S2.doc - Supplemental Material Available under License Creative Commons: Attribution 3.0. Download (76kB) |
Abstract
Successful biological invasion requires introduction of a viable population of a nonindigenous species (NIS). Rarely have ecologists assessed changes in populations while entrained in invasion pathways. Here, we investigate how zooplankton communities resident in ballast water change during transoceanic voyages. We used next-generation sequencing technology to sequence a nuclear small subunit ribosomal DNA fragment of zooplankton from ballast water during initial, middle, and final segments as a vessel transited between Canada and Brazil. Operational taxonomic unit (OTU) diversity decreased as voyage duration increased, indicating loss of community-based genetic diversity and development of bottlenecks for zooplankton taxa prior to discharge of ballast water. On average, we observed 47, 26, and 24 OTUs in initial, middle, and final samples, respectively. Moreover, a comparison of genetic diversity within taxa indicated likely attenuation of OTUs in final relative to initial samples. Abundance of the most common taxa (copepods) declined in all final relative to initial samples. Some taxa (e.g., Copepoda) were represented by a high number of OTUs throughout the voyage, and thus had a high level of intraspecific genetic variation. It is not clear whether genotypes that were most successful in surviving transit in ballast water will be the most successful upon introduction to novel environments. This study highlights that population bottlenecks may be common prior to introduction of NIS to new ecosystems
| Document Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Keywords: | ballast water; biological invasion; genetic diversity; invasive species; Ion torrent PGM; next-generation sequencing; nonindigenous species; zooplankton |
| Research affiliation: | OceanRep > GEOMAR > FB3 Marine Ecology > FB3-EOE-N Experimental Ecology - Food Webs |
| Refereed: | Yes |
| Open Access Journal?: | Yes |
| Publisher: | Wiley |
| Date Deposited: | 02 Jun 2016 08:58 |
| Last Modified: | 01 Feb 2019 15:01 |
| URI: | https://oceanrep.geomar.de/id/eprint/32991 |
Actions (login required)
 |
View Item |
Copyright 2023 | GEOMAR Helmholtz-Zentrum für Ozeanforschung Kiel | All rights reserved
Questions, comments and suggestions regarding the GEOMAR repository are welcomed
at bibliotheksleitung@geomar.de !


 Tools
Tools Tools
Tools
